Potential gradient
Storyboard 
A gradient is a vector that is constructed for a function that indicates the direction and inclination that the function presents at all points. In particular the gradient of the electric potential is equal to minus the electric field.
ID:(1568, 0)
Gradient of a function
Definition 
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
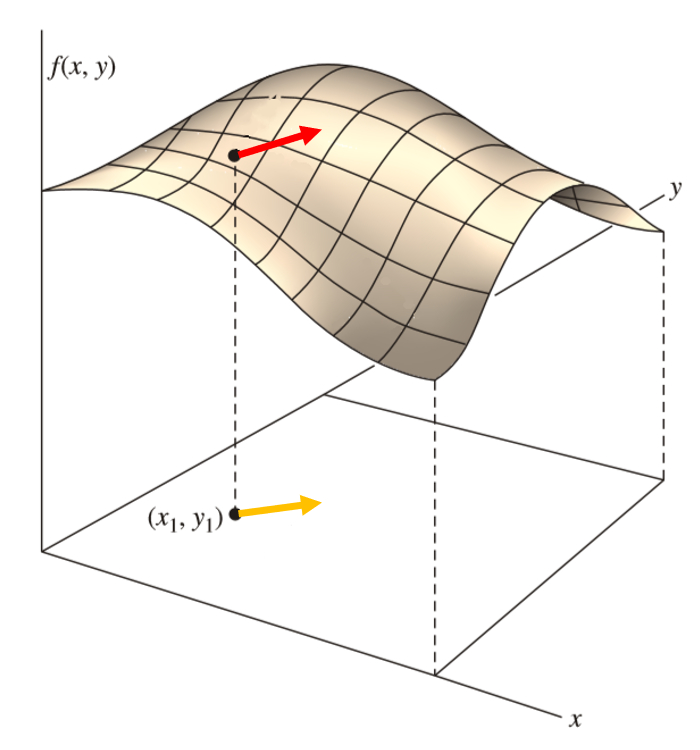
ID:(11555, 0)
Gradient in one dimension
Image 
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered. In the case of a dimension this coincides with the slope of the curve:
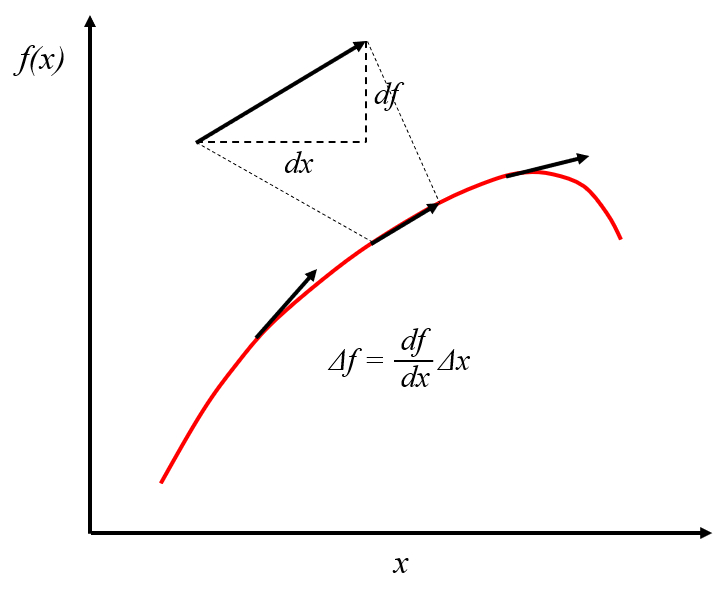
ID:(11558, 0)
Gradient in two dimensions
Note 
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
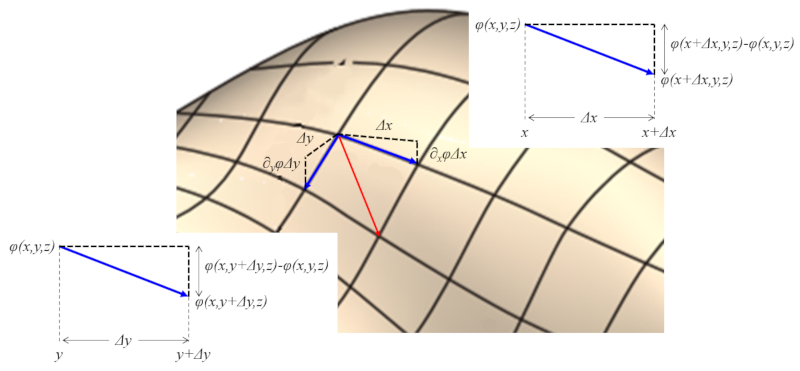
ID:(11605, 0)
Total variation
Quote 
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
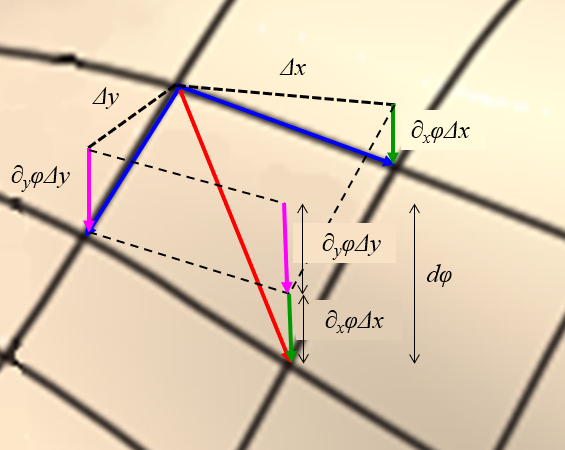
ID:(11606, 0)
Gradient vector: the gradient
Exercise 
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
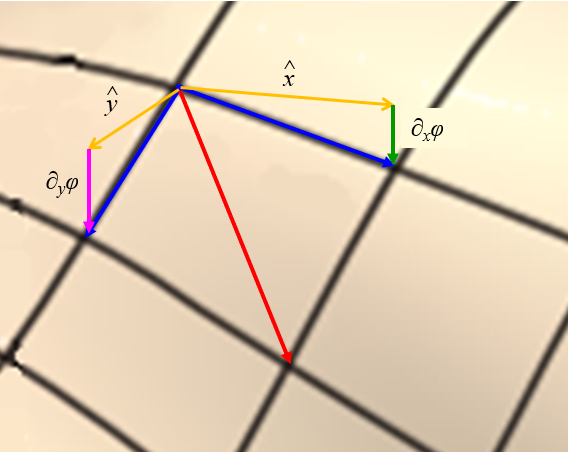
ID:(11607, 0)
Potential gradient
Storyboard 
A gradient is a vector that is constructed for a function that indicates the direction and inclination that the function presents at all points. In particular the gradient of the electric potential is equal to minus the electric field.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Since the infinitesimal variation of potential ($d\varphi$) is the product of the electric field ($\vec{E}$) and the path element traveled ($d\vec{s}$)
and considering the components of the electric field ($\vec{E}$)
$\vec{E} = \hat{x} E_x + \hat{y} E_y + \hat{z} E_z$
along with those of the path element traveled ($d\vec{s}$)
$d\vec{s} = \hat{x} dx + \hat{y} dy + \hat{z} dz$
the expression can be simplified to
$d\varphi = -E_x dx - E_y dy - E_z dz$
With the variation of potential
and the gradient calculated as
it is concluded that the gradient of the potential is equal to the negative of the electric field.
Examples
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered. In the case of a dimension this coincides with the slope of the curve:
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
La variaci n total se puede estimar como la suma de las distintas variaciones.
The gradient is a vector calculated for a function that points to a maximum / minimum close to the point in which it is being considered.
We can construct a vector tangent to the field considering the variation
each component by itself assigning the corresponding versor:
The electric field ($\vec{E}$) is equal to less than the gradient of the electric potential ($\varphi$):
ID:(1568, 0)
