Field divergence
Storyboard 
Divergence analyzes the flow of the electric field for infinitesimal volumes. This value is proportional to the charge density, so the divergence is a tool to detect the presence of charges since the problem of Gauss's law for larger volumes is that if the sum of the charges cancels out within the volume, then also fields tend to offset.
ID:(1566, 0)
Subdividing surfaces and volumes
Image 
Cuando se analizo el flujo eléctrico se vio que se podia calcular sumando las contribuciones de muchas secciones
| $ \Phi = \displaystyle\int \vec{E} \cdot \hat{n} dS $ |
se vio que se podia calcular subdividiendo el volumen en muchas pequeñas superficies
En otras palabras un volumen con su respectiva superficie se puede subdividir en múltiples volúmenes con sus correspondientes superficies:
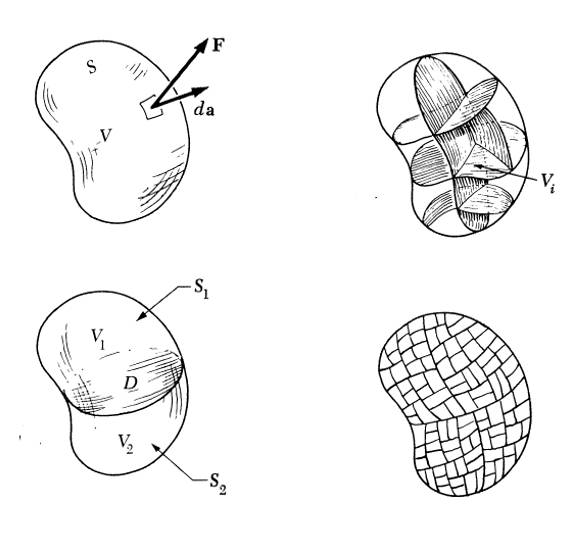
ID:(11560, 0)
Flow by volume
Image 
Si se toma el flujo del campo eléctrico por el volumen en la dirección
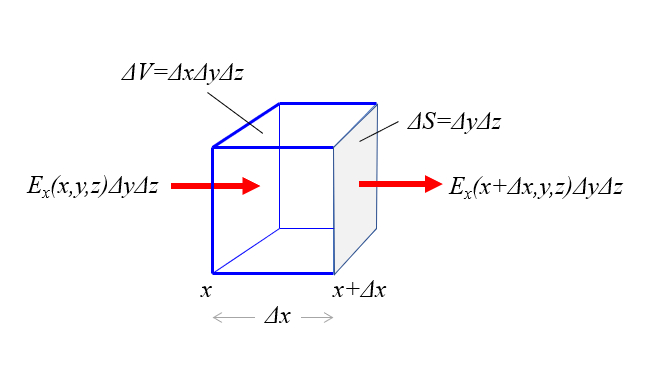
es igual a lo que flujo que sale
ID:(11616, 0)
Field divergence
Model 
Divergence analyzes the flow of the electric field for infinitesimal volumes. This value is proportional to the charge density, so the divergence is a tool to detect the presence of charges since the problem of Gauss's law for larger volumes is that if the sum of the charges cancels out within the volume, then also fields tend to offset.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
None
(ID 11564)
Examples
Cuando se analizo el flujo el ctrico se vio que se podia calcular sumando las contribuciones de muchas secciones
| $ \Phi = \displaystyle\int \vec{E} \cdot \hat{n} dS $ |
se vio que se podia calcular subdividiendo el volumen en muchas peque as superficies
En otras palabras un volumen con su respectiva superficie se puede subdividir en m ltiples vol menes con sus correspondientes superficies:

(ID 11560)
Si se toma el flujo del campo el ctrico por el volumen en la direcci n

es igual a lo que flujo que sale
(ID 11616)
ID:(1566, 0)
