Diagram in momentum-position space $p-q$
Definition 
An analytical technique to analyze motion involves representing momentum as a function of the position of a moving object. This representation enables us to study how momentum evolves with respect to the achieved position.
The representation of motion in the momentum-position space $p-q$ allows us to analyze the displacement's evolution, highlighting extremes in position and momentum.
In the case of periodic motion or when considering the journey both ways, it can be represented as:
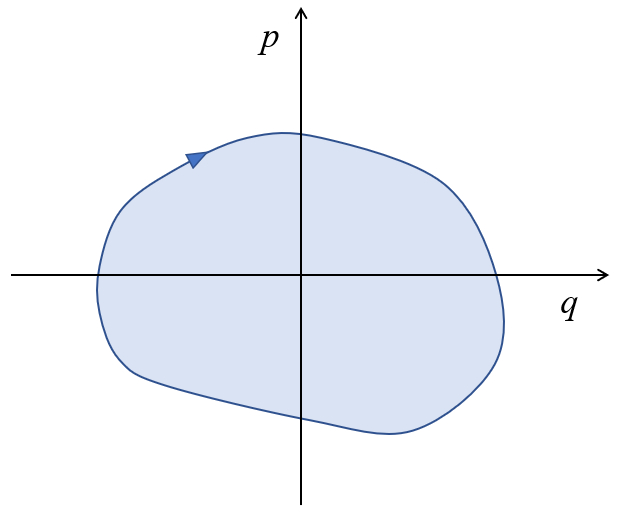
Furthermore, it's evident that the area enclosed by the curve
$\displaystyle\int_{q_1}^{q_2} p dq = \displaystyle\int_{v_1}^{v_2} m v dv = \displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m v_2^2 - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m v_1^2$
corresponds to the system's energy.
The area enclosed by the curve in the momentum-position diagram $p-q$ corresponds to the system's energy.
ID:(1240, 0)
Phase space
Storyboard 
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Given that the kinetic energy is
and the potential energy is
we can express the energy with the radius denoted by the variable $q$ as
In the case where the kinetic energy surpasses the potential energy at the starting radius and the energy is positive (indicating that the object can escape the planet), the equation can be written as
$1 = \left(\displaystyle\frac{p}{\sqrt{2mE}}\right)^2 - \displaystyle\frac{GmM}{Eq}$
which simplifies to
$y=\pm\sqrt{1+\displaystyle\frac{1}{x}}$
with
$x=\displaystyle\frac{q}{GmM/E}$
, and
$y=\displaystyle\frac{p}{2mE}$
In the case where the kinetic energy does not exceed the potential energy (indicating that the object cannot escape the planet's attraction), the energy is negative, and the expression is written as
$1 = -\left(\displaystyle\frac{p}{\sqrt{2mE}}\right)^2 + \displaystyle\frac{GmM}{Eq}$
where $E$ is the absolute value of the energy. With the definitions of $x$ and $y$, we then have
$y=\pm\sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{1}{x}-1}$
The kinetic energy as a function of momentum is given by
and the potential energy as a function of height is
So, if we express the elongation as the position
$x = q$
we obtain
Since kinetic energy is equal to
and momentum is
we can express it as
$K_t=\displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m_i v^2=\displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m_i \left(\displaystyle\frac{p}{m_i}\right)^2=\displaystyle\frac{p^2}{2m_i}$
or
As the kinetic energy as a function of momentum is
and the potential energy as a function of height is
so if the height is expressed as the position
$h = q$
we get
Since in general, energy is the sum of kinetic energy
and potential energy
$E=\displaystyle\frac{p^2}{2m}+U$
If we solve for momentum, we get the following expression:
Examples
An analytical technique to analyze motion involves representing momentum as a function of the position of a moving object. This representation enables us to study how momentum evolves with respect to the achieved position.
The representation of motion in the momentum-position space $p-q$ allows us to analyze the displacement's evolution, highlighting extremes in position and momentum.
In the case of periodic motion or when considering the journey both ways, it can be represented as:
Furthermore, it's evident that the area enclosed by the curve
$\displaystyle\int_{q_1}^{q_2} p dq = \displaystyle\int_{v_1}^{v_2} m v dv = \displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m v_2^2 - \displaystyle\frac{1}{2} m v_1^2$
corresponds to the system's energy.
The area enclosed by the curve in the momentum-position diagram $p-q$ corresponds to the system's energy.
The kinetic energy of a mass $m$
can be expressed in terms of momentum as
If the energy is solved for the momentum, the expressions for positive and negative momentum are obtained:
For the case of a particle in the gravitational field of the Earth, the energy as a function of momentum $p$ and position $q$ is given by
The equation can be written in an adimensional form as
$y=\pm\sqrt{1-x}$
with
$x=\displaystyle\frac{q}{mg/E}$
, and
$y=\displaystyle\frac{p}{\sqrt{2mE}}$
which is represented below
For the case of a mass oscillating with a spring, the energy as a function of momentum $p$ and position $q$ is
The equation can be expressed in an adimensional form as
$1=y^2 + x^2$
where
$x=\displaystyle\frac{q}{\sqrt{2E/k}}$
, and
$y=\displaystyle\frac{p}{\sqrt{2m_iE}}$
solving for
$y=\pm\sqrt{1-x^2}$
Its representation in the xy plane is shown below
For the case of a mass in a gravitational field, the energy as a function of momentum
The equation can be written in an adimensional form for the case of positive energy as (blue and green curves)
$y=\pm\sqrt{1+\displaystyle\frac{1}{x}}$
and for the negative energy case as (red and purple curves)
$y=\pm\sqrt{\displaystyle\frac{1}{x}-1}$
with
$x=\displaystyle\frac{q}{GmM/E}$
, and
$y=\displaystyle\frac{p}{2mE}$
which is depicted below
ID:(1659, 0)
