Darcy's Law
Storyboard 
Hagen-Poiseuille's law for total flow can be redefined in terms of a pressure difference, flow rate, and a factor that can be characterized as hydraulic resistance, thus leading to what is known as Darcy's law.
ID:(877, 0)
Darcy's Law
Storyboard 
Hagen-Poiseuille's law for total flow can be redefined in terms of a pressure difference, flow rate, and a factor that can be characterized as hydraulic resistance, thus leading to what is known as Darcy's law.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
If we consider the profile of ERROR:5449,0 for a fluid in a cylindrical channel, where the speed on a cylinder radio ($v$) varies with respect to ERROR:10120,0 according to the following expression:
involving the tube radius ($R$) and the maximum flow rate ($v_{max}$). We can calculate the maximum flow rate ($v_{max}$) using the viscosity ($\eta$), the pressure difference ($\Delta p$), and the tube length ($\Delta L$) as follows:
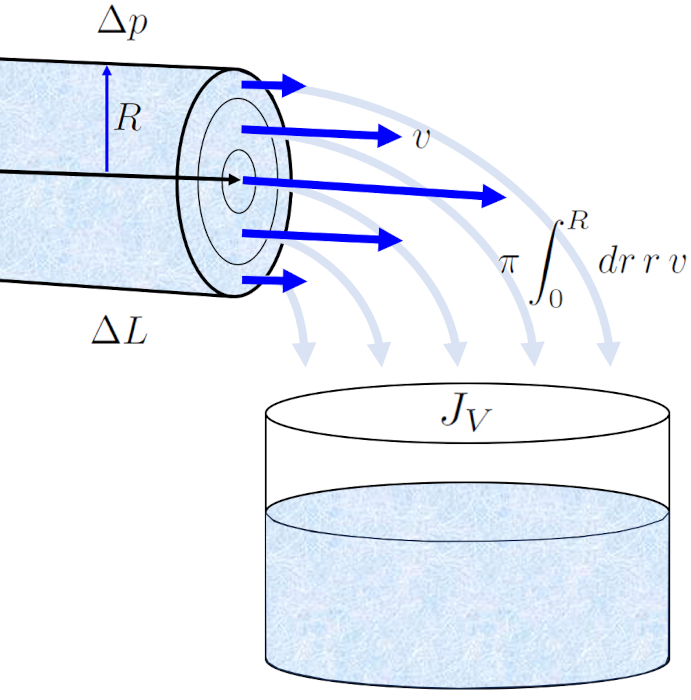
If we integrate the velocity across the cross-section of the channel, we obtain the volume flow ($J_V$), defined as the integral of $\pi r v(r)$ with respect to ERROR:10120,0 from $0$ to ERROR:5417,0. This integral can be simplified as follows:
$J_V=-\displaystyle\int_0^Rdr \pi r v(r)=-\displaystyle\frac{R^2}{4\eta}\displaystyle\frac{\Delta p}{\Delta L}\displaystyle\int_0^Rdr \pi r \left(1-\displaystyle\frac{r^2}{R^2}\right)$
The integration yields the resulting Hagen-Poiseuille law:
The volume flow ($J_V$) can be calculated from the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) and the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) using the following equation:
Furthermore, using the relationship for the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$):
results in:
Since the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) is equal to the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) as per the following equation:
and since the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) is expressed in terms of the viscosity ($\eta$), the tube radius ($R$), and the tube length ($\Delta L$) as follows:
we can conclude that:
If we examine the Hagen-Poiseuille law, which allows us to calculate the volume flow ($J_V$) from the tube radius ($R$), the viscosity ($\eta$), the tube length ($\Delta L$), and the pressure difference ($\Delta p$):
we can introduce the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$), defined in terms of the tube length ($\Delta L$), the tube radius ($R$), and the viscosity ($\eta$), as follows:
to arrive at:
Examples
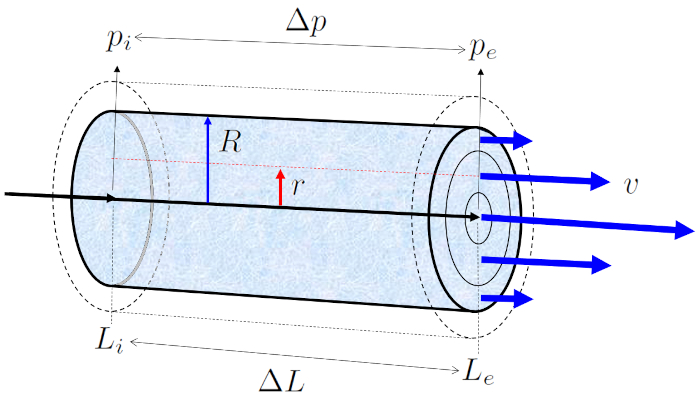
When a tube filled with liquid with a viscosity of ERROR:5422,0 is exposed to the pressure in the initial position ($p_i$) at the position at the beginning of the tube ($L_i$) and the pressure in end position (e) ($p_e$) at the position at the end of the tube ($L_e$), it generates a pressure difference ($\Delta p_s$) along the tube length ($\Delta L$), resulting in the profile of the speed on a cylinder radio ($v$):
In flows with low values of the number of Reynold ($Re$), where viscosity is more significant than the inertia of the liquid, the flow develops in a laminar manner, meaning without the presence of turbulence.
The profile of the speed on a cylinder radio ($v$) in the radius of position in a tube ($r$) allows us to calculate the volume flow ($J_V$) in a tube by integrating over the entire surface, which leads us to the well-known Hagen-Poiseuille law.
The result is an equation that depends on ERROR:5417,0 raised to the fourth power. However, it is crucial to note that this flow profile only holds true in the case of laminar flow.
Thus, from the viscosity ($\eta$), it follows that the volume flow ($J_V$) before ERROR:5430.1 and ERROR:6673.1, the expression:
The original papers that gave rise to this law with a combined name were:
![]() "Ueber die Gesetze, welche des der Strom des Wassers in r hrenf rmigen Gef ssen bestimmen" (On the laws governing the flow of water in cylindrical vessels), Gotthilf Hagen, Annalen der Physik und Chemie 46:423442 (1839).
"Ueber die Gesetze, welche des der Strom des Wassers in r hrenf rmigen Gef ssen bestimmen" (On the laws governing the flow of water in cylindrical vessels), Gotthilf Hagen, Annalen der Physik und Chemie 46:423442 (1839).
![]() "Recherches exp rimentales sur le mouvement des liquides dans les tubes de tr s-petits diam tres" (Experimental research on the movement of liquids in tubes of very small diameters), Jean-Louis-Marie Poiseuille, Comptes Rendus de l'Acad mie des Sciences 9:433544 (1840).
"Recherches exp rimentales sur le mouvement des liquides dans les tubes de tr s-petits diam tres" (Experimental research on the movement of liquids in tubes of very small diameters), Jean-Louis-Marie Poiseuille, Comptes Rendus de l'Acad mie des Sciences 9:433544 (1840).
If we examine the Hagen-Poiseuille law, which allows us to calculate the volume flow ($J_V$) from the tube radius ($R$), the viscosity ($\eta$), the tube length ($\Delta L$), and the pressure difference ($\Delta p$):
we can introduce the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$), defined in terms of the tube length ($\Delta L$), the tube radius ($R$), and the viscosity ($\eta$), as follows:
to arrive at:
Since the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) is equal to the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) as per the following equation:
and since the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) is expressed in terms of the viscosity ($\eta$), the tube radius ($R$), and the tube length ($\Delta L$) as follows:
we can conclude that:
The volume flow ($J_V$) can be calculated from the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) and the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) using the following equation:
Furthermore, using the relationship for the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$):
results in:
which Henry Darcy formulated [1] to model the general behavior of more complex porous media through which a liquid flows.
The genius of this way of rewriting the Hagen-Poiseuille law is that it demonstrates the analogy between the flow of electric current and the flow of liquid. In this sense, Hagen-Poiseuille's law corresponds to Ohm's law. This opens up the possibility of applying the concepts of electrical networks to systems of pipes through which a liquid flows.
This law, also known as the Darcy-Weisbach Law, was first published in Darcy's work:
![]() [1] "Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon" (The Public Fountains of the City of Dijon), Henry Darcy, Victor Dalmont Editeur, Paris (1856).
[1] "Les fontaines publiques de la ville de Dijon" (The Public Fountains of the City of Dijon), Henry Darcy, Victor Dalmont Editeur, Paris (1856).
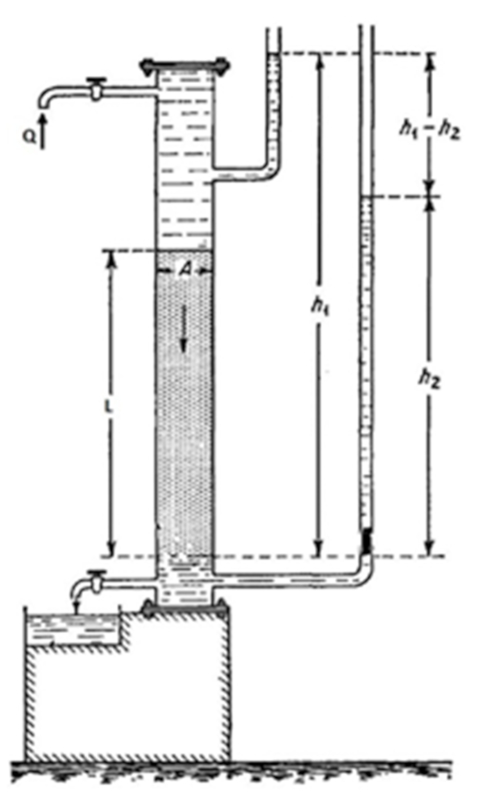
The Darcy\'s experiment involves a cylinder filled with a material under study, which is then filled with the desired liquid. There is a valve at the bottom to regulate the liquid outflow. Both the upper and lower parts have liquid columns associated with them to determine the existing pressures. By measuring the pressures, the amount of flowing liquid, and the elapsed time, the hydraulic resistance can be determined.
The volume flow ($J_V$) can be calculated with the Hagen-Poiseuille law that with the parameters the viscosity ($\eta$), the pressure difference ($\Delta p$), the tube radius ($R$) and the tube length ($\Delta L$) is:
With the tube radius ($R$), the viscosity ($\eta$) and the tube length ($\Delta L$) we have that a hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) is:
With the introduction of the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$), we can rewrite the Hagen-Poiseuille equation with the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) and the volume flow ($J_V$) using the following equation:
In the context of electrical resistance, there exists its inverse, known as electrical conductance. Similarly, what would be the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$) can be defined in terms of the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) through the expression:
Since the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) is equal to the inverse of the hydraulic conductance ($G_h$), it can be calculated from the expression of the latter. In this way, we can identify parameters related to geometry (the tube length ($\Delta L$) and the tube radius ($R$)) and the type of liquid (the viscosity ($\eta$)), which can be collectively referred to as a hydraulic resistance ($R_h$):
Darcy rewrites the Hagen Poiseuille equation so that the pressure difference ($\Delta p$) is equal to the hydraulic resistance ($R_h$) times the volume flow ($J_V$):
ID:(877, 0)