Factor Beta
Equation
La proporción de la velocidad con la velocidad de la luz se define como el factor $\beta$:
$\beta=\displaystyle\frac{v}{c}$
ID:(4822, 0)
Factor de Lorentz
Equation
El factor que define la dilatación temporal y contracción espacial es el factor de Lorentz:
$\gamma=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-\beta^2}}$
ID:(4823, 0)
Photon Energy jumping between Orbits
Equation
$E_{nm}=Ry Z^2\left(\displaystyle\frac{1}{n^2}-\displaystyle\frac{1}{m^2}\right)$
ID:(4044, 0)
Potencia de Bremsstrahlung para aceleración paralela
Equation
La potencia irradiada ante aceleración en la dirección de desplazamiento es
$P_{a||v}=\displaystyle\frac{q^2a^2\gamma^6}{6\pi\epsilon_0c^3}$
ID:(4826, 0)
Potencia de Bremsstrahlung para aceleración perpendicular
Equation
La potencia irradiada ante aceleración en la dirección perpendicular de desplazamiento es
$P_{a\perp v}=\displaystyle\frac{q^2a^2\gamma^4}{6\pi\epsilon_0c^3}$
ID:(4827, 0)
Calculated path of speed
Concept
If we consider an area with width $\Delta t$ on a velocity versus time graph, it represents the displacement during that time:
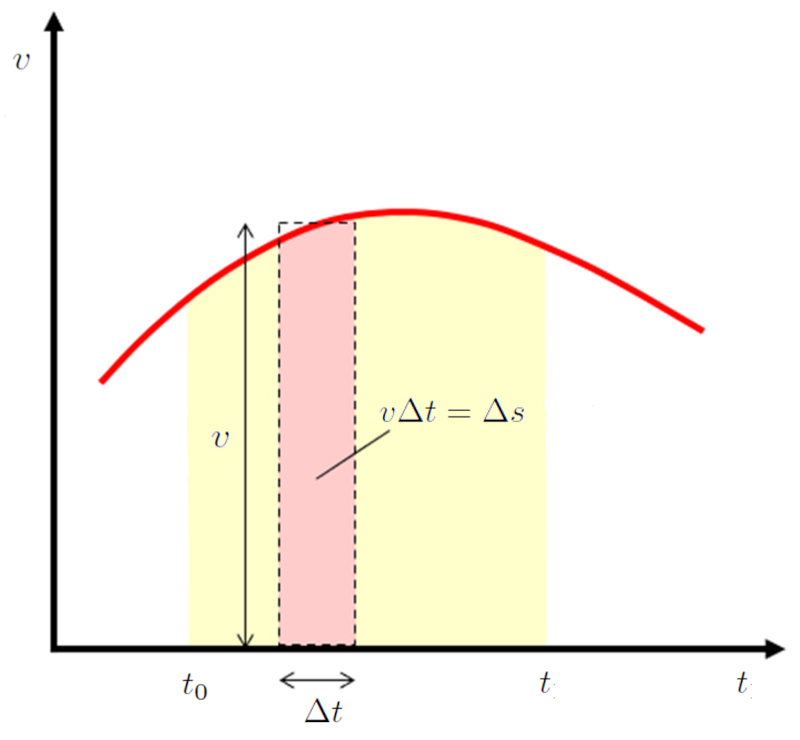
In the particular case where acceleration is constant, velocity is represented on the velocity versus time graph as a straight line. This line is defined by the speed ($v$), the initial Speed ($v_0$), the constant Acceleration ($a_0$), the time ($t$), and the start Time ($t_0$), equal to:
| $ v = v_0 + a_0 ( t - t_0 )$ |
and is graphed as follows:
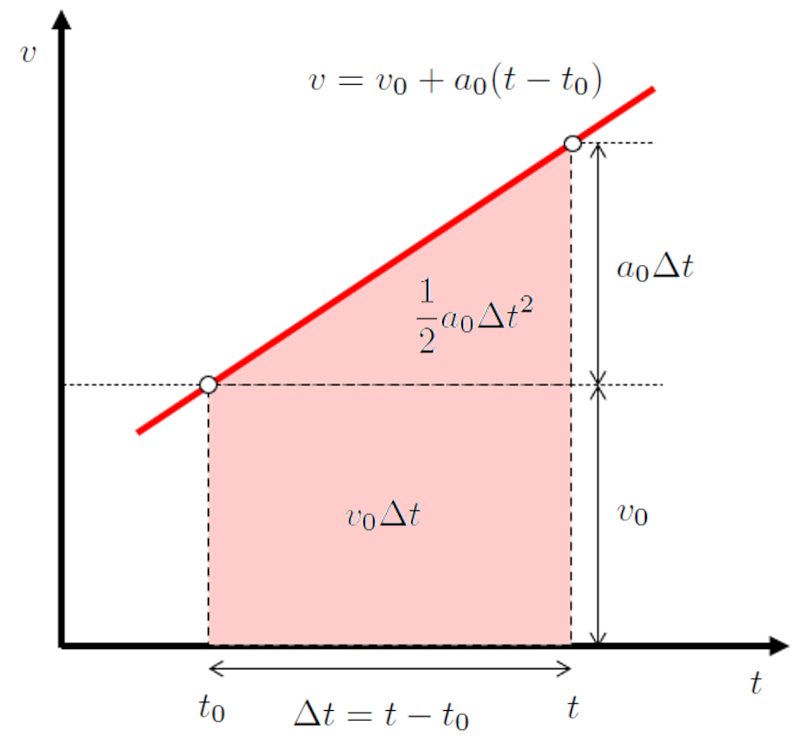
Since the area under the curve can be represented as the sum of a rectangle with area
$v_0(t-t_0)$
and a triangle with area
$\displaystyle\frac{1}{2}a_0(t-t_0)^2$
We can calculate the displacement the distance traveled in a time ($\Delta s$) from the position ($s$) and the starting position ($s_0$), leading us to:
| $ \Delta s \equiv s - s_0 $ |
Therefore, the position ($s$) is equal to:
| $ s = s_0 + v_0 ( t - t_0 )+\displaystyle\frac{1}{2} a_0 ( t - t_0 )^2$ |
ID:(4828, 0)
Two-stage movement
Concept
In a scenario of movement in two stages, first the object modifies its velocity by the speed difference in the first stage ($\Delta v_1$) during a time interval of ($$) with an acceleration of ($$).
Subsequently, in the second stage, it progresses by modifying its velocity by the speed difference in the second stage ($\Delta v_2$) during a time interval of the time spent in the second stage ($\Delta t_2$) with an acceleration of the acceleration during the second stage ($a_2$).
When represented graphically, we obtain a velocity and time diagram as shown below:
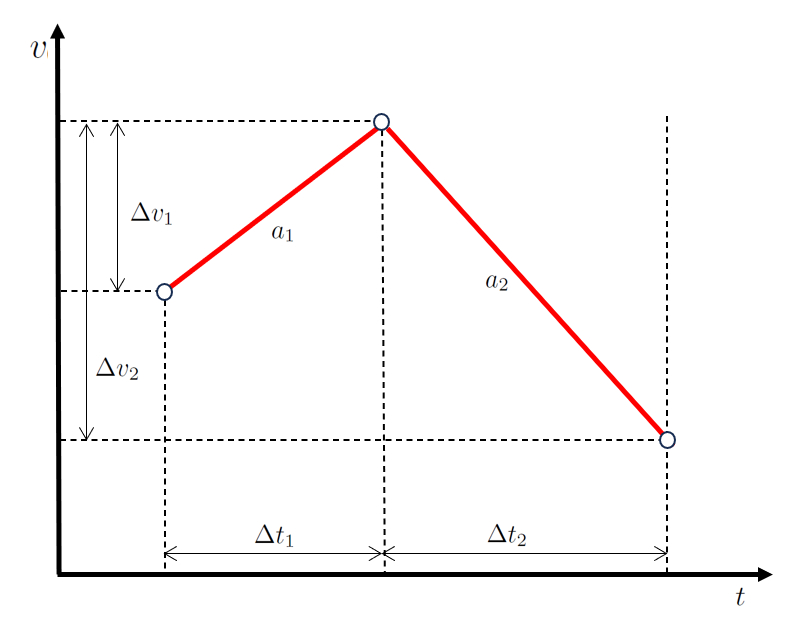
The key here is that the values the time spent in the first stage ($\Delta t_1$) and the time spent in the second stage ($\Delta t_2$) are sequential, just like the values the speed difference in the first stage ($\Delta v_1$) and the speed difference in the second stage ($\Delta v_2$).
ID:(4829, 0)
Potencia media
Equation
La potencia se define como la variación del trabajo en el tiempo lo que se expresa como
La potencia se define como la variación del trabajo
| $ \Delta W = W - W_0 $ |
en el tiempo
| $ \Delta t \equiv t - t_0 $ |
lo que se expresa como
| $ P =\displaystyle\frac{ \Delta W }{ \Delta t }$ |
La potencia es clave para entender las limitantes que tienen los sistemas para obtener o entregar energía limitando la forma como se comportan los objetos.
Los sistemas tienen un limite en la potencia que pueden generar (la energía que puede generar un sistema por unidad de tiempo) lo que limita su capacidad para cambiar la dinamica.
ID:(4439, 0)
