Gaussian distribution
Storyboard 
In the limit of similar probabilities the binomial distribution is reduced in the continuous limit to the Gaussean distribution.
ID:(1556, 0)
Example comparison with Gaussian distribution
Definition 
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
| $P(x)=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}e^{-(x-\mu)^2/2\sigma^2}$ |
which is represented below:
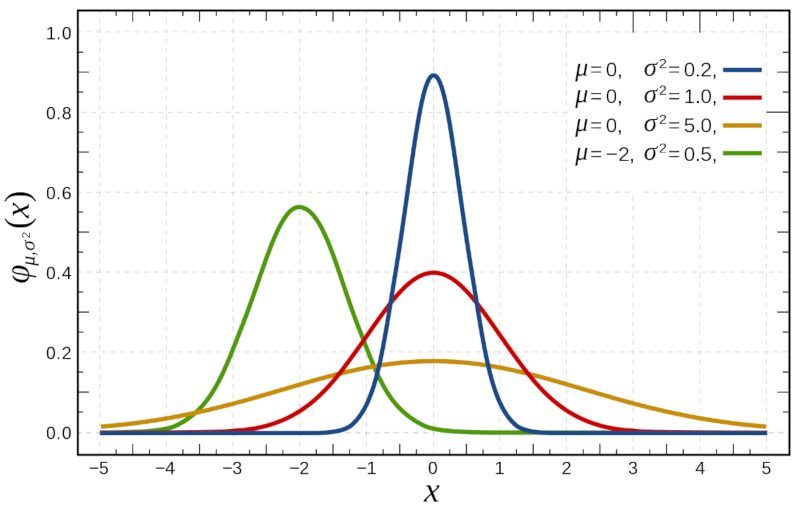
ID:(7793, 0)
Gaussian distribution
Storyboard 
In the limit of similar probabilities the binomial distribution is reduced in the continuous limit to the Gaussean distribution.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
Con
con
y solo existe la probabilidad de ir a la derecha o a la izquierda, con
por lo que con
With the Stirling approximation
and the change of variables
you get that
With the Stirling approximation
and the change of variables
you get that
With the Stirling approximation
and the change of variables
the expression is
In the case of medium probabilities (
and
is obtained
The expression
is reduced by
to representation
If total
To obtain the Gaussian distribution it is necessary to develop the distribution around its deviation from its mean position that can be given by
As the way is
factor
As the way is
factor
If large numbers and probabilities around 1/2 are entered in the binomial distribution for the case
the expressions
and
a distribution of the form is obtained
To develop the
With the approximation
it has to
To develop the factor
With the approximation
it has to
It can be shown that for a large number
In this case, the probability
$\begin{matrix}
P(x) & = & \displaystyle\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}}e^{-(x-\mu)^2/2\sigma^2}\\
\sigma^2 & = & Np(1-p)\\
\end{matrix}
$
The standard deviation of the binomial distribution at the limit
If we study the binomial distribution for large numbers
which is represented below:
ID:(1556, 0)
