Sound propagation
Storyboard 
The sound wave is propagated so that its energy per area element is reduced as it moves away from the source.
ID:(386, 0)
Propagation depending on the Intensity at source
Definition 
Si se considera una esfera en torno de la fuente a un radio
$W=4\pi r_0^2 I_0$
por lo que la intensidad es con
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{1}{4 \pi }\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ r ^2}$ |
a una distancia
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{ r_0 ^2}{ r ^2} I_0 $ |
ID:(15567, 0)
Propagation of the intensity
Image 
Si consideramos una fuente puntual, la intensidad del sonido es con
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ S }$ |
se propagara en forma esférica. En este caso la superficie es con
| $ S = 4 \pi r ^2$ |
con lo que la intensidad es con
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{1}{4 \pi }\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ r ^2}$ |
ID:(15566, 0)
Propagation of Sound
Note 
Sound propagates and interacts with various edges and objects. On flat surfaces it is reflected under the same angle it affects (ground, building). However, the wind leads to refraction with what the beams bend:
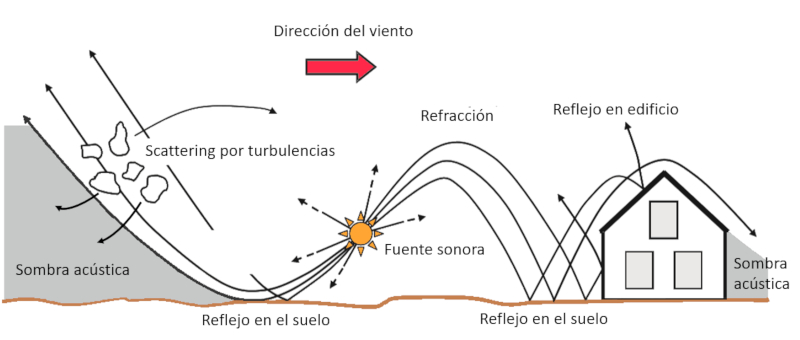
ID:(516, 0)
Spherical propagation
Quote 
For a point source, the sound spreads in all directions uniformly. Therefore, the sound level will be reduced due to the effect that the energy is distributed over a surface of a sphere of radius
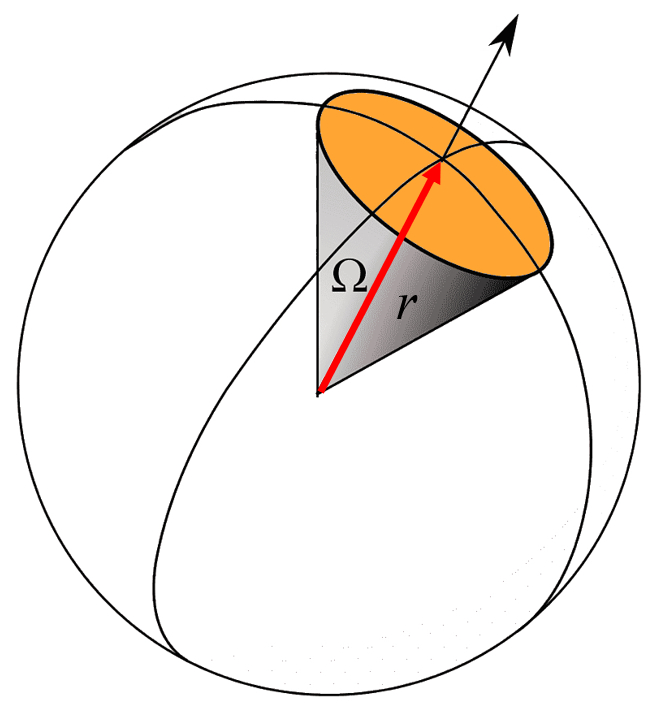
ID:(11829, 0)
Sum of intensities and powers
Exercise 
Since the different beams do not interact, the intensity and power that occurs at any point in space is equal to the sum of the individual contributions:
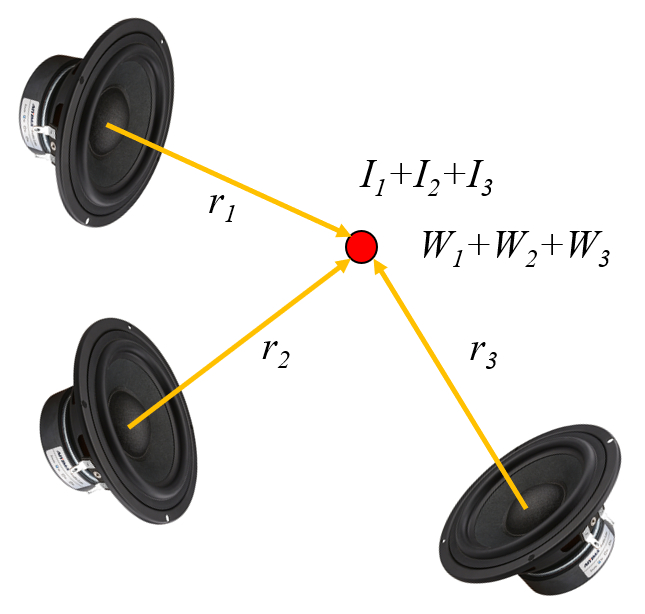
ID:(11830, 0)
Sound propagation
Storyboard 
The sound wave is propagated so that its energy per area element is reduced as it moves away from the source.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
Sound propagates and interacts with various edges and objects. On flat surfaces it is reflected under the same angle it affects (ground, building). However, the wind leads to refraction with what the beams bend:
For a point source, the sound spreads in all directions uniformly. Therefore, the sound level will be reduced due to the effect that the energy is distributed over a surface of a sphere of radius
Si consideramos una fuente puntual, la intensidad del sonido es con
se propagara en forma esf rica. En este caso la superficie es con
con lo que la intensidad es con
Si se considera una esfera en torno de la fuente a un radio
$W=4\pi r_0^2 I_0$
por lo que la intensidad es con
a una distancia
Since the different beams do not interact, the intensity and power that occurs at any point in space is equal to the sum of the individual contributions:
Como los distintos haces no interactuan la intensidad que se da en cualquier punto del espacio es igual a la suma de las contribuciones individuales.
Con
Si consideramos una fuente puntual, la intensidad del sonido es con
se propagara en forma esf rica. En este caso la superficie es con
con lo que la intensidad es con
Si se considera una esfera en torno de la fuente a un radio
$W=4\pi r_0^2 I_0$
por lo que la intensidad es con
a una distancia
Just like in other human sensory systems, our hearing is capable of detecting pressure variations over a wide range $(10^{-5}-10^2 Pa)$. However, when we perceive a signal doubling, it doesn't correspond to double the pressure or sound intensity, but rather the square of these magnitudes. In other words, our signal detection capacity operates on a logarithmic and nonlinear scale.
Hence, the noise level ($L$) is indicated not in the sound Intensity ($I$) or the reference intensity ($I_{ref}$), but in the base ten logarithm of these magnitudes. Particularly, we take the lowest sound intensity we can perceive, the reference intensity ($I_{ref}$)
, and use it as a reference. The new scale is defined with
The sound pressure level that we can detect with our ear, denoted as the reference pressure, water ($p_{ref}$), is $2 \times 10^{-5} , Pa$.
Since the sound Intensity ($I$) is associated with the sound pressure ($p_s$), the mean density ($\rho$), and the speed of sound ($c$), and is equal to
we can calculate a value for the reference intensity ($I_{ref}$) based on the value of the reference pressure, water ($p_{ref}$):
This is achieved with a density of $1.27 , kg/m^3$ and a sound speed of $331 , m/s$, equivalent to $9.5 \times 10^{-13} , W/m^2$.
The noise level ($L$) encompasses a wide range of the sound pressure ($p_s$), making it useful to define a scale that mitigates this difficulty. To do so, we can work with the logarithm of the pressure normalized by a value corresponding to zero on this scale. If we take the minimum pressure that a person can detect, defined as the reference pressure ($p_{ref}$), we can define a scale using:
which starts at 0 for the audible range. In the case of air, the reference pressure ($p_{ref}$) is $20 \mu Pa$.
ID:(386, 0)
