Thermal Radiation
Storyboard 
The thermal energy of a body is stored in the form of oscillations of atoms in it. By having electric charges atoms the movement of these functions as an antenna emitting energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. In this way the bodies emit heat even if they are not in contact with an external medium.
ID:(314, 0)
Radiation
Note 
Charged particles that oscillate displace their surrounding electric field, generating electromagnetic oscillations. In our world, these oscillations are known as radiation, and depending on their frequency or wavelength, they can manifest as heat, light, or radio waves.
For the particle in question, the emission of radiation corresponds to a loss of energy, and thus, a loss of heat. Similarly, when the particle absorbs radiation from the electromagnetic field in its vicinity, its energy increases, leading to an increase in its temperature.
ID:(204, 0)
Thermal Radiation
Description 
The thermal energy of a body is stored in the form of oscillations of atoms in it. By having electric charges atoms the movement of these functions as an antenna emitting energy in the form of electromagnetic waves. In this way the bodies emit heat even if they are not in contact with an external medium.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
(ID 15272)
(ID 15331)
Charged particles that oscillate displace their surrounding electric field, generating electromagnetic oscillations. In our world, these oscillations are known as radiation, and depending on their frequency or wavelength, they can manifest as heat, light, or radio waves.
For the particle in question, the emission of radiation corresponds to a loss of energy, and thus, a loss of heat. Similarly, when the particle absorbs radiation from the electromagnetic field in its vicinity, its energy increases, leading to an increase in its temperature.
(ID 204)
Radiators are heated using water that is heated in a central boiler and circulated through the heating system. The heated water warms the metal of the radiators, which, on one hand, heats the surrounding air through convection, creating warmth in the room. They also emit infrared radiation, which can be captured photographically, as illustrated in the following image:
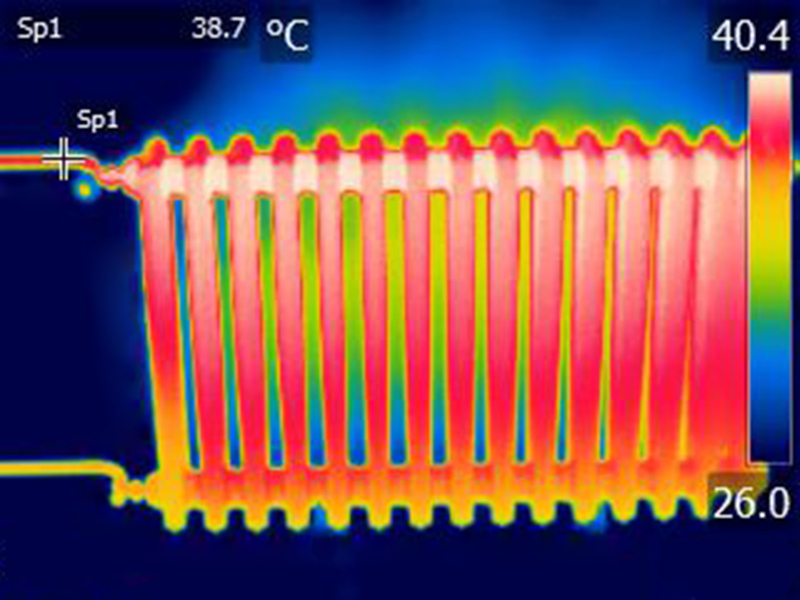
(ID 11196)
ID:(314, 0)
