The bone
Definition 
We will work with a bone and with the fall and impact scenarios. The bone parameters and material properties are summarized here:

Geometry and elasticity
ID:(1556, 0)
The dynamics
Image 
Two situations are considered, fall (break due to buckling, compression or flexion) and impact on the central part of the bone (break due to flexion).

ID:(1557, 0)
Impact fracture
Exercise 
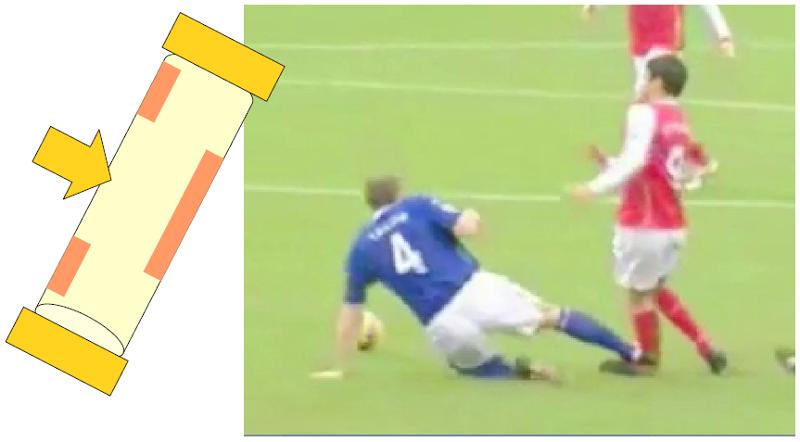
If a player is impacted in the middle of the bone, considering the foot due to friction and the body due to inertia as fixed points, it results in a load that flexes the bone.
None
Question of interest: What are the energy, stress, force, displacement, and jump height at which buckling would occur? ($W_{tv}$, $\sigma_{tv}$, $F_{tv}$, $u_{tv}$, $v$).
ID:(1560, 0)
Deportes y Fracturas
Storyboard 
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
The energy required for an object to change its angular velocity from $\omega_1$ to $\omega_2$ can be calculated using the definition
Applying Newton's second law, this expression can be rewritten as
$\Delta W=I \alpha \Delta\theta=I\displaystyle\frac{\Delta\omega}{\Delta t}\Delta\theta$
Using the definition of angular velocity
we get
$\Delta W=I\displaystyle\frac{\Delta\omega}{\Delta t}\Delta\theta=I \omega \Delta\omega$
The difference in angular velocities is
$\Delta\omega=\omega_2-\omega_1$
On the other hand, angular velocity itself can be approximated with the average angular velocity
$\omega=\displaystyle\frac{\omega_1+\omega_2}{2}$
Using both expressions, we obtain the equation
$\Delta W=I \omega \Delta \omega=I(\omega_2-\omega_1)\displaystyle\frac{(\omega_1+\omega_2)}{2}=\displaystyle\frac{I}{2}(\omega_2^2-\omega_1^2)$
Thus, the change in energy is given by
$\Delta W=\displaystyle\frac{I}{2}\omega_2^2-\displaystyle\frac{I}{2}\omega_1^2$
This allows us to define kinetic energy as
As the gravitational force is
with $m$ representing the mass. To move this mass from a height $h_1$ to a height $h_2$, a distance of
is covered. Therefore, the energy
with $\Delta s=\Delta h$ gives us the variation in potential energy:
$\Delta W = F\Delta s=mg\Delta h=mg(h_2-h_1)=U_2-U_1=\Delta V$
thus, the gravitational potential energy is
The work variance ($\Delta W$) required for an object to change from the initial Angular Speed ($\omega_0$) to the angular Speed ($\omega$) is obtained by applying a the torque ($T$) that produces an angular displacement the difference of Angles ($\Delta\theta$), according to:
Applying Newton's second law for rotation, in terms of the moment of inertia for axis that does not pass through the CM ($I$) and the mean Angular Acceleration ($\bar{\alpha}$):
this expression can be rewritten as:
$\Delta W = I \alpha \Delta\theta$
or, using the difference in Angular Speeds ($\Delta\omega$) and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$):
we get:
$\Delta W = I\displaystyle\frac{\Delta\omega}{\Delta t} \Delta\theta$
Using the definition of the mean angular velocity ($\bar{\omega}$) and the time elapsed ($\Delta t$):
results in:
$\Delta W = I\displaystyle\frac{\Delta\omega}{\Delta t} \Delta\theta = I\omega \Delta\omega$
where the difference in Angular Speeds ($\Delta\omega$) is expressed as:
On the other hand, the angular velocity can be approximated by the average angular velocity:
$\bar{\omega}=\displaystyle\frac{\omega_1 + \oemga_2}{2}$
By combining both expressions, we obtain the equation:
$\Delta W = I \omega \Delta\omega = I(\omega_2 - \omega_1) \displaystyle\frac{(\omega_1 + \omega_2)}{2} = \displaystyle\frac{I}{2}(\omega_2^2 - \omega_1^2)$
Therefore, the change in energy is expressed as:
$\Delta W = \displaystyle\frac{I}{2}\omega_2^2 - \displaystyle\frac{I}{2}\omega_1^2$
This allows us to define the rotational kinetic energy as:
Examples
We will work with a bone and with the fall and impact scenarios. The bone parameters and material properties are summarized here:
Two situations are considered, fall (break due to buckling, compression or flexion) and impact on the central part of the bone (break due to flexion).
If a player is impacted in the middle of the bone, considering the foot due to friction and the body due to inertia as fixed points, it results in a load that flexes the bone.
Question of interest: What are the energy, stress, force, displacement, and jump height at which buckling would occur? ($W_{tv}$, $\sigma_{tv}$, $F_{tv}$, $u_{tv}$, $v$).
$V=\pi r^2h$
The translational Kinetic Energy ($K_t$) is determined based on the speed ($v$) and the inertial Mass ($m_i$), according to:
5288 is associated with 6290 and not with 8762, even though they are numerically equal. The energy that an object possesses is a direct consequence of the inertia that had to be overcome to set it in motion.
The relationship between the angle
To calculate the corresponding function can be used
The kinetic energy of rotation ($K_r$) is a function of the angular Speed ($\omega$) and of a measure of inertia represented by the moment of inertia for axis that does not pass through the CM ($I$):
The relationship between the angle
To calculate the corresponding function can be used
The total Kinetic Energy ($K$) can have translational and/or rotational components. Therefore, it is expressed as the sum of the translational Kinetic Energy ($K_t$) and the kinetic energy of rotation ($K_r$):
The relationship between the angle
To calculate the corresponding function can be used
At the surface of the planet, the gravitational force is
and the energy
can be shown to be
ID:(457, 0)
