Force of gravity and tides in conjunction
Storyboard 
Gravity and centrifugal acceleration generate tides, the movement of oceans that raises and lowers their level with a frequency of 12 hours. Their origin can be generated by both the moon and the sun.
ID:(1523, 0)
Force of gravity and tides in conjunction
Storyboard 
Gravity and centrifugal acceleration generate tides, the movement of oceans that raises and lowers their level with a frequency of 12 hours. Their origin can be generated by both the moon and the sun.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
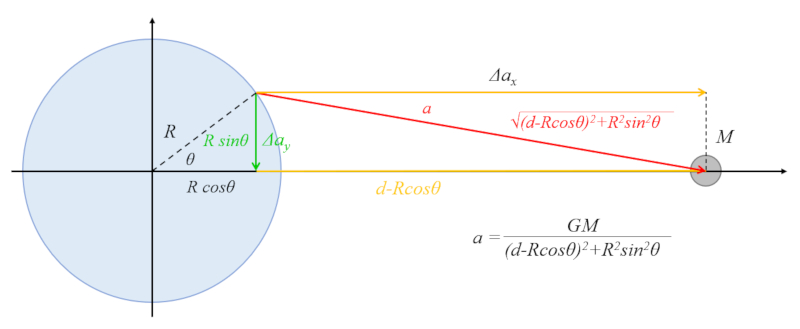
There is a contribution from the gravitational attraction of the celestial body that pulls water towards the equatorial region:
The hypotenuse of the triangle is related to the vertical leg by:
$R\sin\theta$
and the horizontal leg by:
$d - R\cos\theta$
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we have:
$R^2\sin^2\theta+(d-R\cos\theta)^2=d^2+R^2-2Rd\cos\theta$
There is a contribution from the gravitational attraction of the celestial body that pulls water towards the radius, which tends to displace the water towards the equatorial zone:
The hypotenuse of the triangle is formed by the vertical leg:
$R\sin\theta$
and the horizontal leg:
$d - R\cos\theta$
According to the Pythagorean theorem, we have:
$R^2\sin^2\theta+(d-R\cos\theta)^2=d^2+R^2-2Rd\cos\theta$
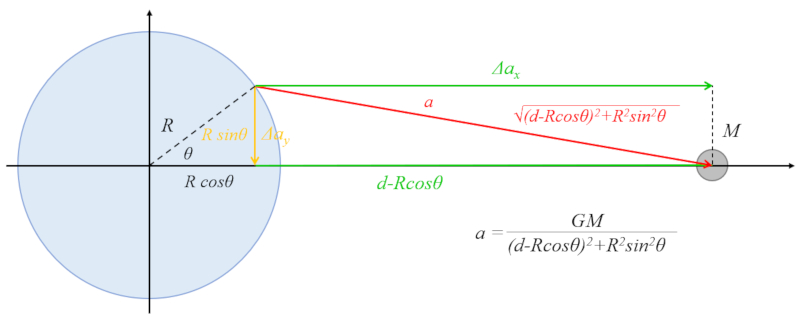
To determine the variation of the acceleration perpendicular to the radius, we can use triangle similarity to equate the relation
$\displaystyle\frac{\Delta a_{cy}}{a_c}$
with the length
$d-R\cos\theta$
and the hypotenuse
$\sqrt{d^2+R^2-2dR\cos\theta}$
.
By triangle similarity, we have with
Con la ley de la gravitaci n de Newton, con
Se puede, con la definici n de la fuerza, con
Y el radio al cuadrado:
$r^2=d^2+R^2-2dR\cos\theta$
Calcular la aceleraci n reemplazando el radio en la fuerza y despejando la aceleraci n. Esto da con
With
And since the expression for acceleration is with
It follows that:
$\Delta a_{cy} = GM\displaystyle\frac{R\sin\theta}{(d^2 + R^2 - 2dR\cos\theta)^{3/2}}\sim \displaystyle\frac{GM}{d^2}\displaystyle\frac{R\sin\theta}{d}$
Therefore, in the approximation
To determine the variation of the acceleration parallel to the radius, we can use triangle similarity to equate the relation
$\displaystyle\frac{\Delta a_{cx}}{a_c}$
with the length
$d+R\cos\theta$
and the hypotenuse
$\sqrt{d^2+R^2-2dR\cos\theta}$
By triangle similarity, we have with
With
And as for
Thus, we have:
$\Delta a_{cx} =GM\displaystyle\frac{d - R\cos\theta}{(d^2 + R^2 - 2dR\cos\theta)^{3/2}}\sim \displaystyle\frac{GM}{d^2}\left(1+\displaystyle\frac{2R\cos\theta}{d}\right)$
Therefore, in the approximation
ID:(1523, 0)