Sound propagation
Storyboard 
The sound wave is propagated so that its energy per area element is reduced as it moves away from the source.
ID:(386, 0)
Sound propagation
Description 
The sound wave is propagated so that its energy per area element is reduced as it moves away from the source.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
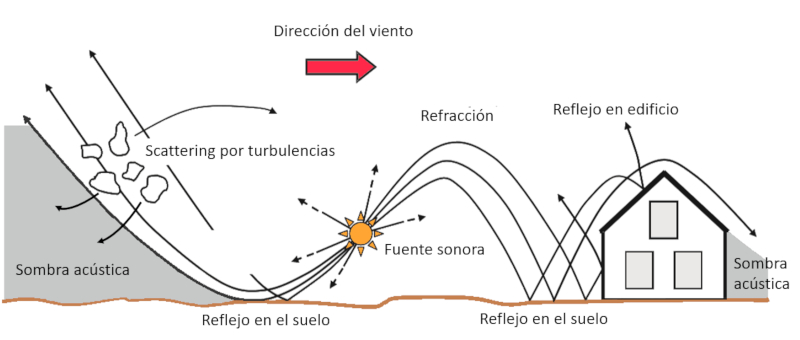
Sound propagates and interacts with various edges and objects. On flat surfaces it is reflected under the same angle it affects (ground, building). However, the wind leads to refraction with what the beams bend:
(ID 516)
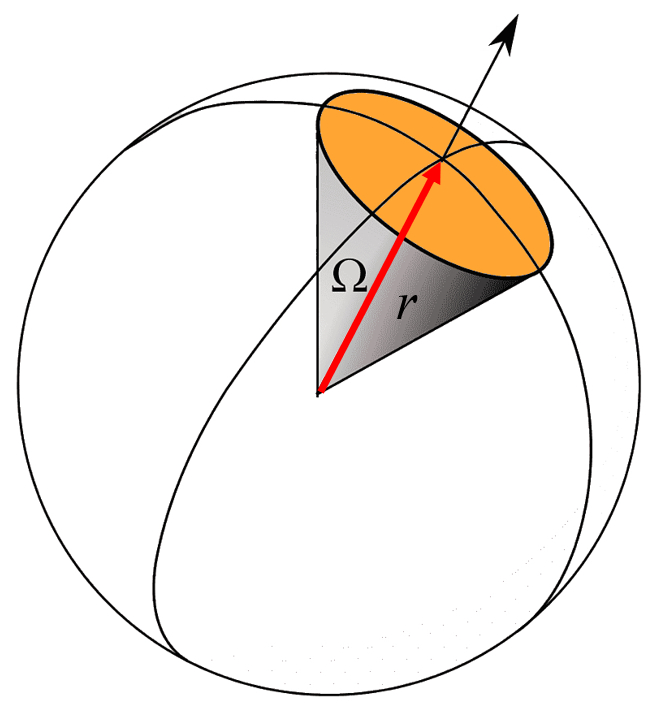
For a point source, the sound spreads in all directions uniformly. Therefore, the sound level will be reduced due to the effect that the energy is distributed over a surface of a sphere of radius
(ID 11829)
Si consideramos una fuente puntual, la intensidad del sonido es con
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ S }$ |
se propagara en forma esf rica. En este caso la superficie es con
| $ S = 4 \pi r ^2$ |
con lo que la intensidad es con
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{1}{4 \pi }\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ r ^2}$ |
(ID 15566)
Si se considera una esfera en torno de la fuente a un radio
$W=4\pi r_0^2 I_0$
por lo que la intensidad es con distance between Emitter and Receiver $m$, intensity in the distance $W/m^2$ and sound Power $W$
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{1}{4 \pi }\displaystyle\frac{ P }{ r ^2}$ |
a una distancia
| $ I =\displaystyle\frac{ r_0 ^2}{ r ^2} I_0 $ |
(ID 15567)
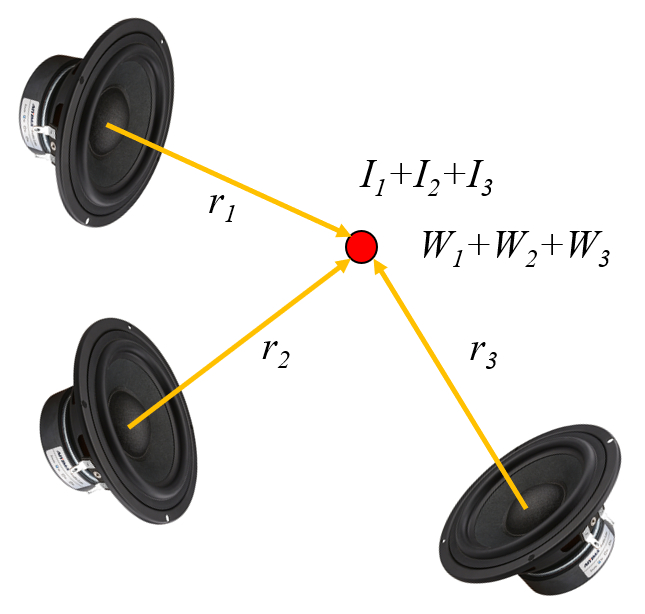
Since the different beams do not interact, the intensity and power that occurs at any point in space is equal to the sum of the individual contributions:
(ID 11830)
(ID 15455)
ID:(386, 0)
