Velocity of Sound in the Sea
Storyboard 
The speed of sound in the sea depends on the pressure, temperature and salinity.
ID:(1548, 0)
Speed of sound with depth
Image 
The speed of sound in the ocean varies with depth as shown in the graph:
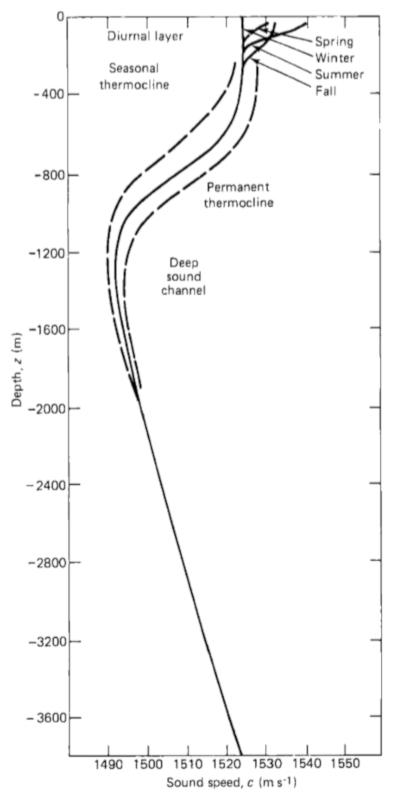
The shape of the curve can vary depending on the time of year.
ID:(11814, 0)
Dependence on the speed of sound
Note 
The speed of sound in the ocean depends on the temperature and pressure as shown in the graph:
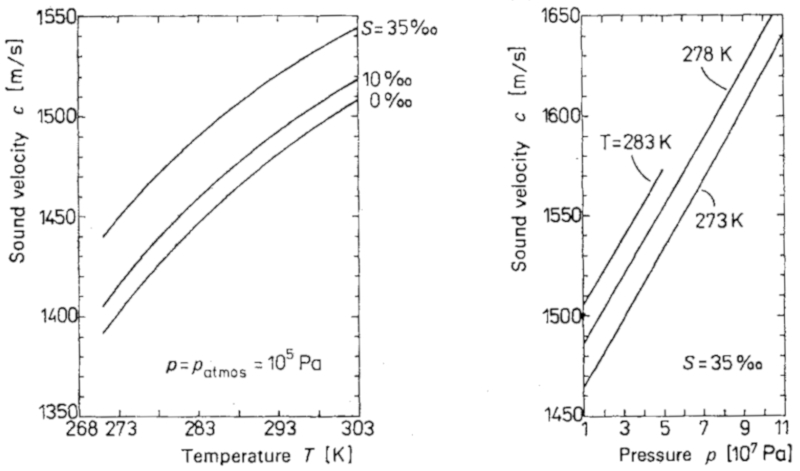
ID:(11815, 0)
Velocity of Sound in the Sea
Storyboard 
The speed of sound in the sea depends on the pressure, temperature and salinity.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Observando la imagen se nota que los senos de los angulos son respectivamente\\n\\n
$\sin\theta_i=\displaystyle\frac{c_i\Delta t}{d}$
y\\n\\n
$\sin\theta_e=\displaystyle\frac{c_e\Delta t}{d}$
\\n\\nSi se despeja en ambas ecuaciones la distancia
$d=\displaystyle\frac{c_i\Delta t}{\sin\theta_i}=\displaystyle\frac{c_e\Delta t}{\sin\theta_e}$
por lo que se tiene que
Observando la imagen se nota que los senos de los angulos son respectivamente\\n\\n
$\sin\theta_i=\displaystyle\frac{c_i\Delta t}{d}$
y\\n\\n
$\sin\theta_e=\displaystyle\frac{c_e\Delta t}{d}$
\\n\\nSi se despeja en ambas ecuaciones la distancia
$d=\displaystyle\frac{c_i\Delta t}{\sin\theta_i}=\displaystyle\frac{c_e\Delta t}{\sin\theta_e}$
por lo que se tiene que
Given that the photon frequency ($\nu$) is the inverse of the period ($T$):
$\nu=\displaystyle\frac{1}{T}$
this means that the speed of Light ($c$) is equal to the distance traveled in one oscillation, which is ERROR:8439, divided by the elapsed time, which corresponds to the period:
$c=\displaystyle\frac{\lambda}{T}$
In other words, the following relationship holds:
Given that the photon frequency ($\nu$) is the inverse of the period ($T$):
$\nu=\displaystyle\frac{1}{T}$
this means that the speed of Light ($c$) is equal to the distance traveled in one oscillation, which is ERROR:8439, divided by the elapsed time, which corresponds to the period:
$c=\displaystyle\frac{\lambda}{T}$
In other words, the following relationship holds:
Examples
The speed of sound in the ocean varies with depth as shown in the graph:
The shape of the curve can vary depending on the time of year.
The speed of sound in the ocean depends on the temperature and pressure as shown in the graph:
In 1977, Clay and Medwin developed a model to estimate the speed of sound based on temperature, salinity, and pressure.
the speed of sound ($c$) can be estimated based on the presión hidrostatica ($p$), the temperature ($T$), and the salinity ($s$) using the following expression:
where $c_i$ are empirical constants.
Reference: "Study of Absorption loss effects on acoustic wave propagation in shallow water using different empirical Models", Yasin Yousif Al-Aboosi, Mustafa Sami Ahmed, Nor Shahida Mohd Shah, and Nor Hisham Haji Khamis, ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 12, No. 22, November 2017.
La relaci n entre los ngulos de incidencia y refractados indicados en la siguiente gr fica
se pueden escribir en funci n de la velocidad de la luz en cada medio
La relaci n entre los ngulos de incidencia y refractados indicados en la siguiente gr fica
se pueden escribir en funci n de la velocidad de la luz en cada medio
In 1977, Clay and Medwin developed a model to estimate the speed of sound based on temperature, salinity, and pressure.
the speed of sound ($c$) can be estimated based on the presión hidrostatica ($p$), the temperature ($T$), and the salinity ($s$) using the following expression:
where $c_i$ are empirical constants.
Reference: "Study of Absorption loss effects on acoustic wave propagation in shallow water using different empirical Models", Yasin Yousif Al-Aboosi, Mustafa Sami Ahmed, Nor Shahida Mohd Shah, and Nor Hisham Haji Khamis, ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 12, No. 22, November 2017.
In 1977, Clay and Medwin developed a model to estimate the speed of sound based on temperature, salinity, and pressure.
the speed of sound ($c$) can be estimated based on the presión hidrostatica ($p$), the temperature ($T$), and the salinity ($s$) using the following expression:
where $c_i$ are empirical constants.
Reference: "Study of Absorption loss effects on acoustic wave propagation in shallow water using different empirical Models", Yasin Yousif Al-Aboosi, Mustafa Sami Ahmed, Nor Shahida Mohd Shah, and Nor Hisham Haji Khamis, ARPN Journal of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Vol. 12, No. 22, November 2017.
A wave of the photon frequency ($\nu$) is related to ERROR:8439 through the speed of Light ($c$), according to the following formula:
This formula corresponds to the mechanical relationship stating that the speed of a wave is equal to its wavelength (distance traveled) divided by the period of oscillation, or equivalently, directly proportional to the frequency (the inverse of the period).
A wave of the photon frequency ($\nu$) is related to ERROR:8439 through the speed of Light ($c$), according to the following formula:
This formula corresponds to the mechanical relationship stating that the speed of a wave is equal to its wavelength (distance traveled) divided by the period of oscillation, or equivalently, directly proportional to the frequency (the inverse of the period).
ID:(1548, 0)
