Refrigerators
Storyboard 
Refrigeration is an inverse process of the internal combustion machine. In this case, work is supplied by which heat is extracted from a thermodynamic system.
ID:(1489, 0)
Elements of a refrigerator
Image 
If you observe a refrigerator, you can relatively easily identify the different parts that compose it. These are:
• Evaporator (which absorbs heat). This component operates by evaporating the refrigerant liquid to absorb heat from inside the refrigerator.
• Compressor. The compressor transfers the vapor generated by the evaporator, compresses it, and pushes it towards the condenser.
• Condenser (which emits heat). In the condenser, the vapor condenses, releasing energy that is radiated into the environment through the grille usually located at the back of the refrigerator.
• Expansion valve, which allows the liquid to return to the evaporator.
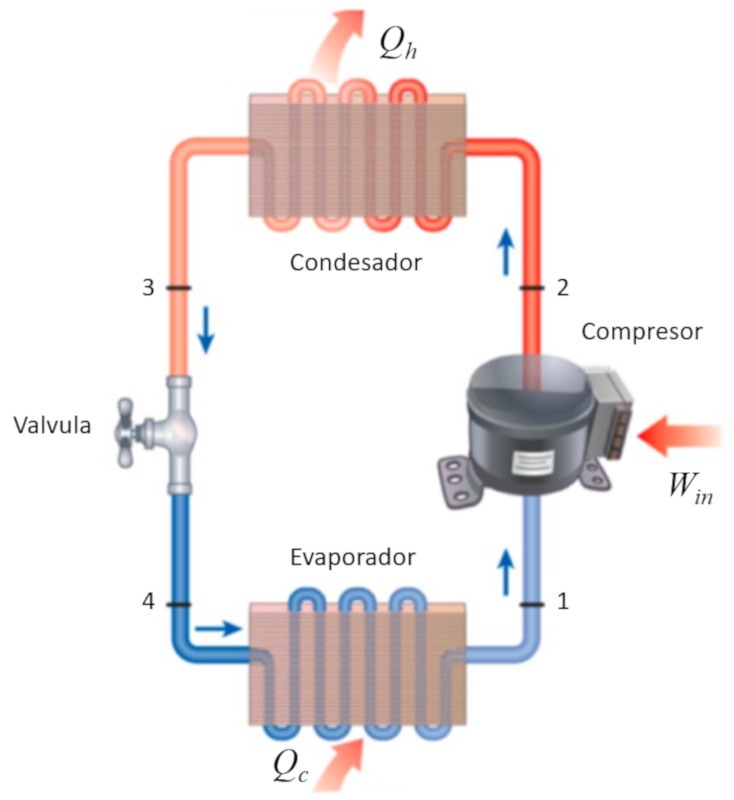
ID:(11167, 0)
Heat pump application: the refrigerator
Description 
If you observe a refrigerator, you can relatively easily identify the different parts that compose it. These are:
• Evaporator (which absorbs heat). This component operates by evaporating the refrigerant liquid to absorb heat from inside the refrigerator.
• Compressor. The compressor transfers the vapor generated by the evaporator, compresses it, and pushes it towards the condenser.
• Condenser (which emits heat). In the condenser, the vapor condenses, releasing energy that is radiated into the environment through the grille usually located at the back of the refrigerator.
• Expansion valve, which allows the liquid to return to the evaporator.
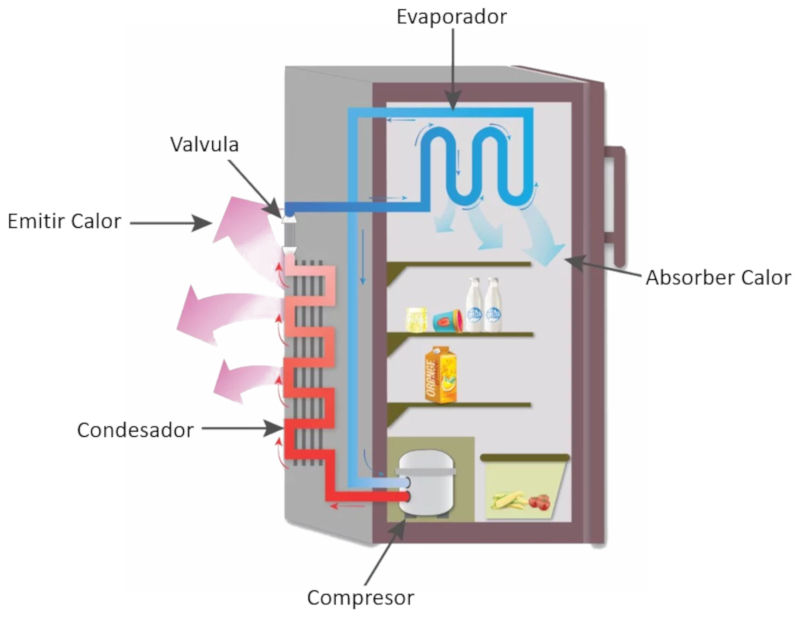
ID:(11166, 0)
Carnot cycle for refrigeration
Description 
If the Carnot process is reversed, it can be used to transfer heat using work, which is known as a heat pump. In this case, the diagram is as follows:
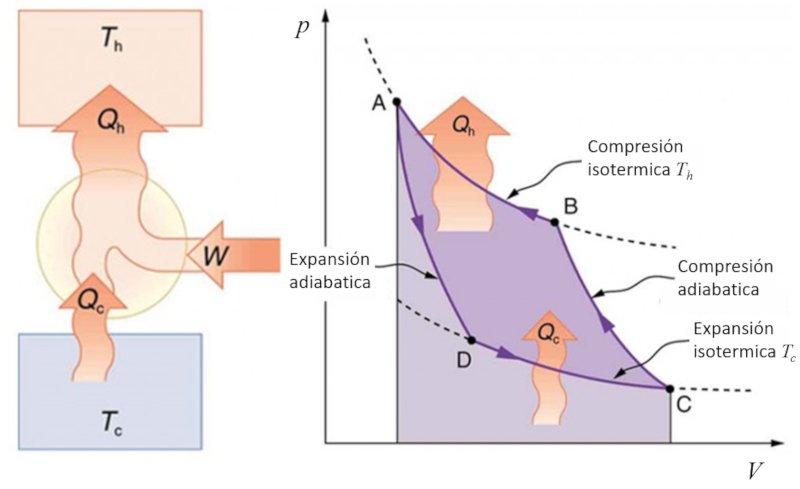
ID:(11143, 0)
Concept of a heat pump
Description 
A heat pump is a way to implement the reverse Carnot process, which involves using work to transfer heat from a colder body to a hotter one.
A heat pump includes two key components:
• An evaporator (which absorbs heat)
• A compressor (which releases heat)
It also has a circuit to move the vapor and liquid:
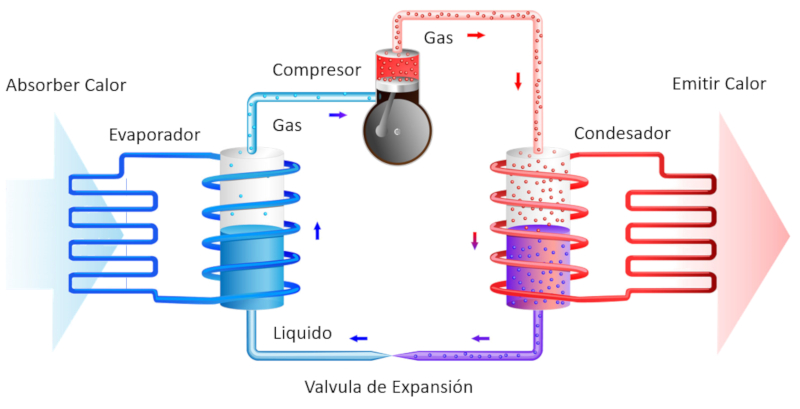
ID:(11165, 0)
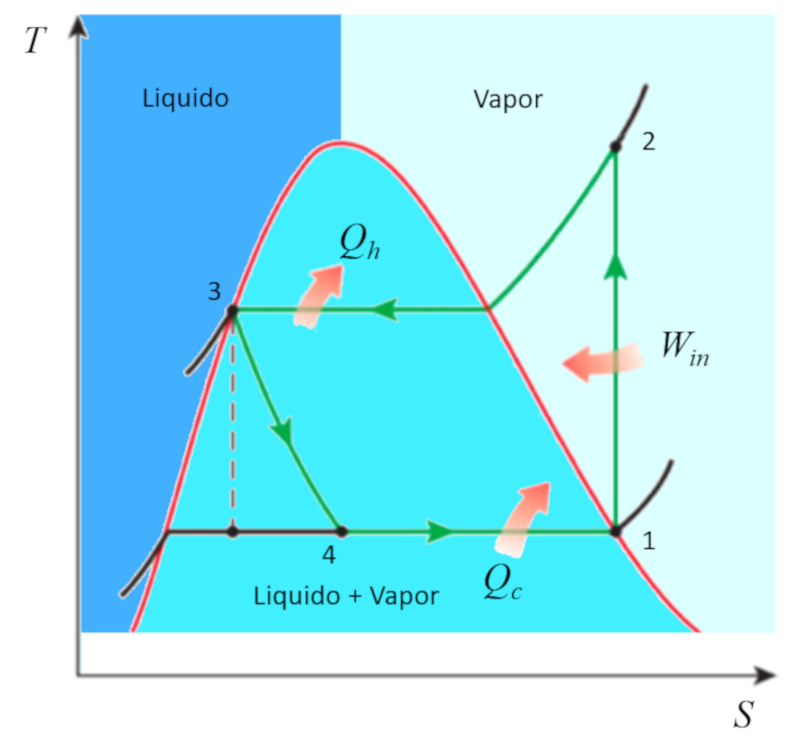
Temperature and entropy diagram in case of refrigeration
Description 
The temperature-entropy diagram contains three regions that represent different states. These are:
• Liquid
• Vapor
• Liquid-vapor mixture
The process itself involves the following stages:
1 to 2: Application of work
2 to 3: Heat rejection in the condenser
3 to 4: Expansion in the expansion valve
4 to 1: Heat absorption in the evaporator
ID:(11168, 0)
Refrigerators
Model 
Refrigeration is an inverse process of the internal combustion machine. In this case, work is supplied by which heat is extracted from a thermodynamic system.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
If you observe a refrigerator, you can relatively easily identify the different parts that compose it. These are:
• Evaporator (which absorbs heat). This component operates by evaporating the refrigerant liquid to absorb heat from inside the refrigerator.
• Compressor. The compressor transfers the vapor generated by the evaporator, compresses it, and pushes it towards the condenser.
• Condenser (which emits heat). In the condenser, the vapor condenses, releasing energy that is radiated into the environment through the grille usually located at the back of the refrigerator.
• Expansion valve, which allows the liquid to return to the evaporator.

(ID 11167)
If you observe a refrigerator, you can relatively easily identify the different parts that compose it. These are:
• Evaporator (which absorbs heat). This component operates by evaporating the refrigerant liquid to absorb heat from inside the refrigerator.
• Compressor. The compressor transfers the vapor generated by the evaporator, compresses it, and pushes it towards the condenser.
• Condenser (which emits heat). In the condenser, the vapor condenses, releasing energy that is radiated into the environment through the grille usually located at the back of the refrigerator.
• Expansion valve, which allows the liquid to return to the evaporator.

(ID 11166)
(ID 15285)
(ID 15344)
If the Carnot process is reversed, it can be used to transfer heat using work, which is known as a heat pump. In this case, the diagram is as follows:

(ID 11143)
A heat pump is a way to implement the reverse Carnot process, which involves using work to transfer heat from a colder body to a hotter one.
A heat pump includes two key components:
• An evaporator (which absorbs heat)
• A compressor (which releases heat)
It also has a circuit to move the vapor and liquid:

(ID 11165)
The temperature-entropy diagram contains three regions that represent different states. These are:
• Liquid
• Vapor
• Liquid-vapor mixture
The process itself involves the following stages:
1 to 2: Application of work
2 to 3: Heat rejection in the condenser
3 to 4: Expansion in the expansion valve
4 to 1: Heat absorption in the evaporator

(ID 11168)
ID:(1489, 0)
