Generalized Force
Storyboard 
The generalized forces (intensive variables) and their corresponding conjugate variables (extensive variables) represent how various microscopic parameters can be calculated from microscopic distributions.
ID:(438, 0)
Examples of intensive and extensive variables
Image 
An article that summarizes most of the thermodynamic relationships very well is Use of Legendre Transforms in Chemical Thermodynamics, Robert A. Alberty, Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 73, No. 8, pp. 13491380, 2001 containing the following table of pairs of extensive and intensive variables:
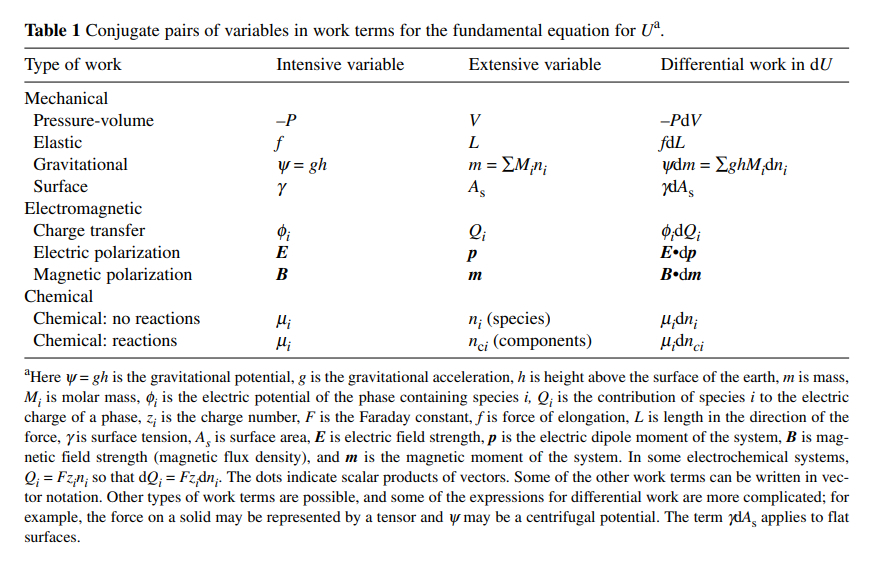
ID:(11545, 0)
Generalized Force
Model 
The generalized forces (intensive variables) and their corresponding conjugate variables (extensive variables) represent how various microscopic parameters can be calculated from microscopic distributions.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
Examples
An article that summarizes most of the thermodynamic relationships very well is Use of Legendre Transforms in Chemical Thermodynamics, Robert A. Alberty, Pure Appl. Chem., Vol. 73, No. 8, pp. 13491380, 2001 containing the following table of pairs of extensive and intensive variables:

(ID 11545)
ID:(438, 0)
