Colors and Photons
Storyboard 
Light, in its corpuscular picture, is described by introducing a particle that we call the photon.
Its color is a reflection of its energy being the frequency of this directly proportional to this.
ID:(668, 0)
The spectre
Definition 
As the angle of refraction depends on the frequency or wavelength of light in glass, a prism can be used to decompose light into its different colors.
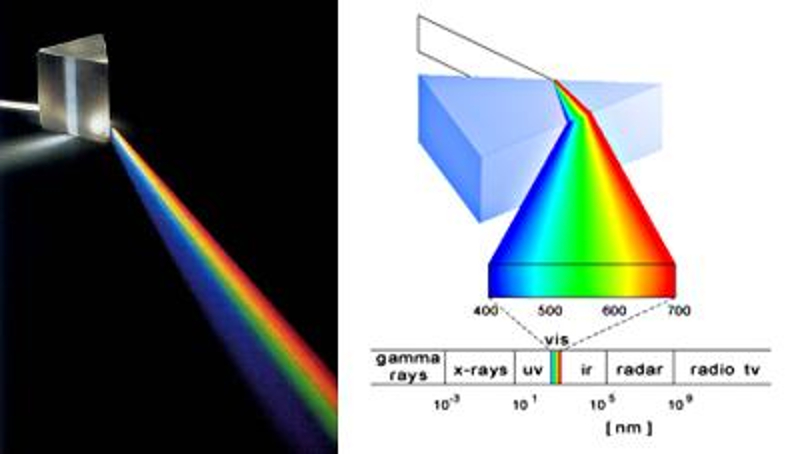
This results in what we call the spectrum of light.
ID:(6972, 0)
Colors and Photons
Description 
Light, in its corpuscular picture, is described by introducing a particle that we call the photon. Its color is a reflection of its energy being the frequency of this directly proportional to this.
Variables
Calculations
Calculations
Equations
(ID 3341)
Examples
As the angle of refraction depends on the frequency or wavelength of light in glass, a prism can be used to decompose light into its different colors.

This results in what we call the spectrum of light.
(ID 6972)
The color of light is associated with its the photon frequency ($\nu$), and there is a direct relationship between this frequency and the photon energy ($\epsilon$):
| $ \epsilon = h \nu $ |
where the planck constant ($h$) has a value of $6.62\times 10^{-34} , \text{Js}$.
(ID 3341)
ID:(668, 0)
