Propagation
Storyboard 
The propagation of light in a homogeneous medium occurs rectilinearly at a characteristic speed that depends on both the medium and the frequency (color) of the light.
Propagation can be described both as a corpuscular model, in which the particles are called photons, as a wave model.
ID:(300, 0)
Light
Definition 
Light is an electromagnetic wave with a wavelength $\lambda$ that falls within the range of 380 nm to 750 nm, encompassing the visible spectrum that our eyes can perceive.

Light propagates in a straight line and can undergo refraction, meaning it can be deviated, if the speed of light changes due to the medium it passes through.
ID:(408, 0)
Propagation of light in a straight line and in a spherical shape
Image 
Light travels in a straight line and radiates spherically around its source.
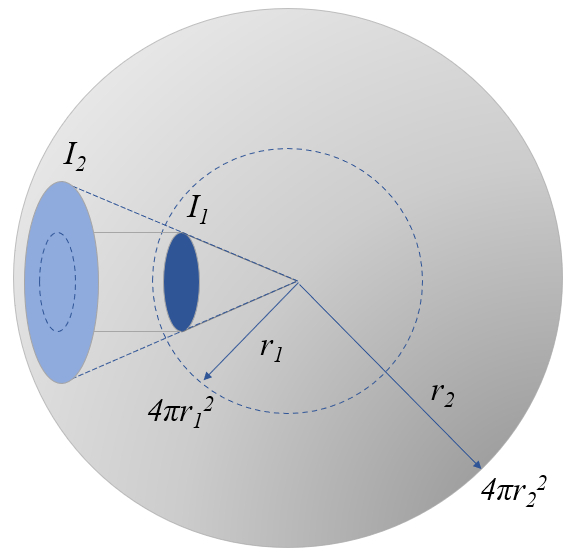
Because of this spherical distribution, its intensity decreases with distance from the source.
ID:(12677, 0)
Non-uniform emission: orifice
Note 
When light passes through an aperture, it does not propagate uniformly but instead exhibits a distribution, creating what is known as a penumbra.
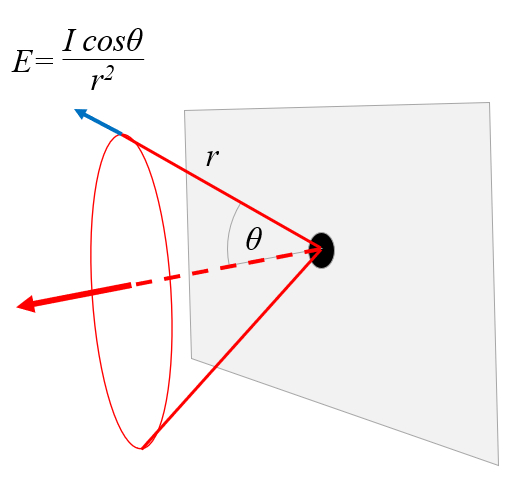
ID:(12679, 0)
